About
Introduction
In order to support students, the DesUni model creates a learning environment that puts the students in a Design-Thinking frame of mind in their work with the curriculum. The DesUni model is about supporting the students in becoming the primary agents in the teaching process, and in changing their expectations from being theoretically instructed as passive receivers of knowledge, to becoming active creators of knowledge.
Design is, in our opinion, a creative approach to constructing new knowledge and solving problems that are grounded in a particular set of hands-on methods, experimental co-creation processes and open mind-sets. In order to make students act and think in a design-oriented way, it is necessary to activate the students’ imagination.
Why do we need the DesUni teaching model? We teach students how to make and use patterns. DesUni helps us teach students how to break existing patterns and experiment with ‘what might be?’ The approach supports students in activating not only their formal and explicit knowledge, but also the endless amount of knowledge hidden within their imagination. DesUni learning is working with the university curriculum in a more creative and innovative way. It gives students competences to change ‘what is’ and develop preferred new futures and the competences called for by today’s societies and companies. DesUni is a valuable supplement, or alternative, to traditional university teaching models.
Whilst the aim of the DesUni model is NOT to make students designers, it does support students in thinking and acting like designers, in their work with the curriculum. To us, design is a creative approach to constructing new knowledge and problem solving.
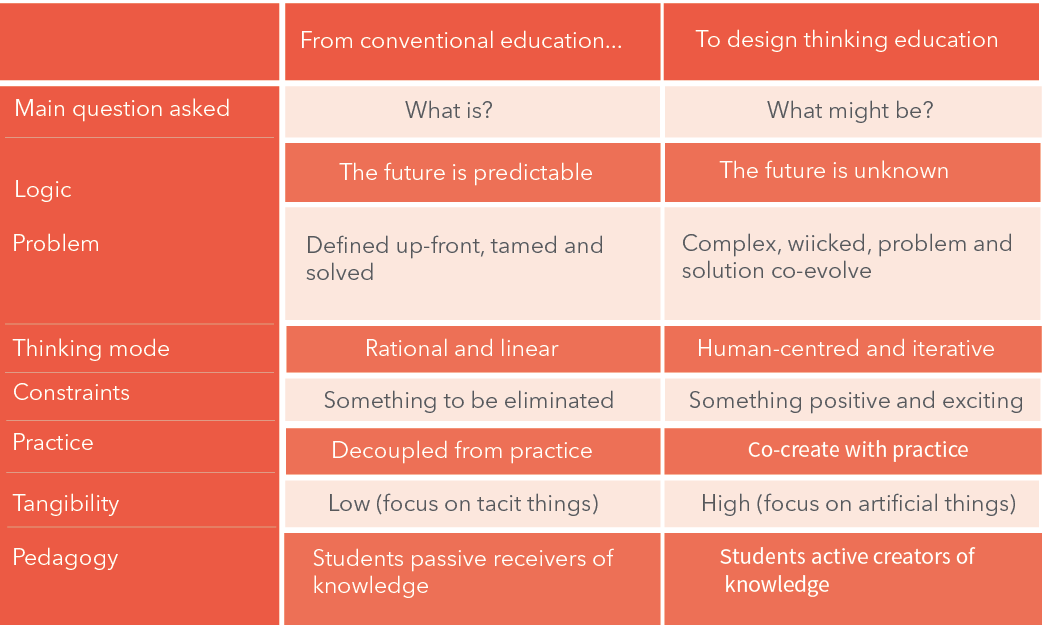
The differences between much contemporary education, based on the rationale of causation, and DesUni education based on DesUni learning and Design Thinking, is sketched out in Table 1. This indirectly indicates that tensions exist between much contemporary education and Design Thinking.
Table 1. The tension between much contemporary education and Design Thinking
The three inner elements of the DesUni model
Surrounding the student in the center
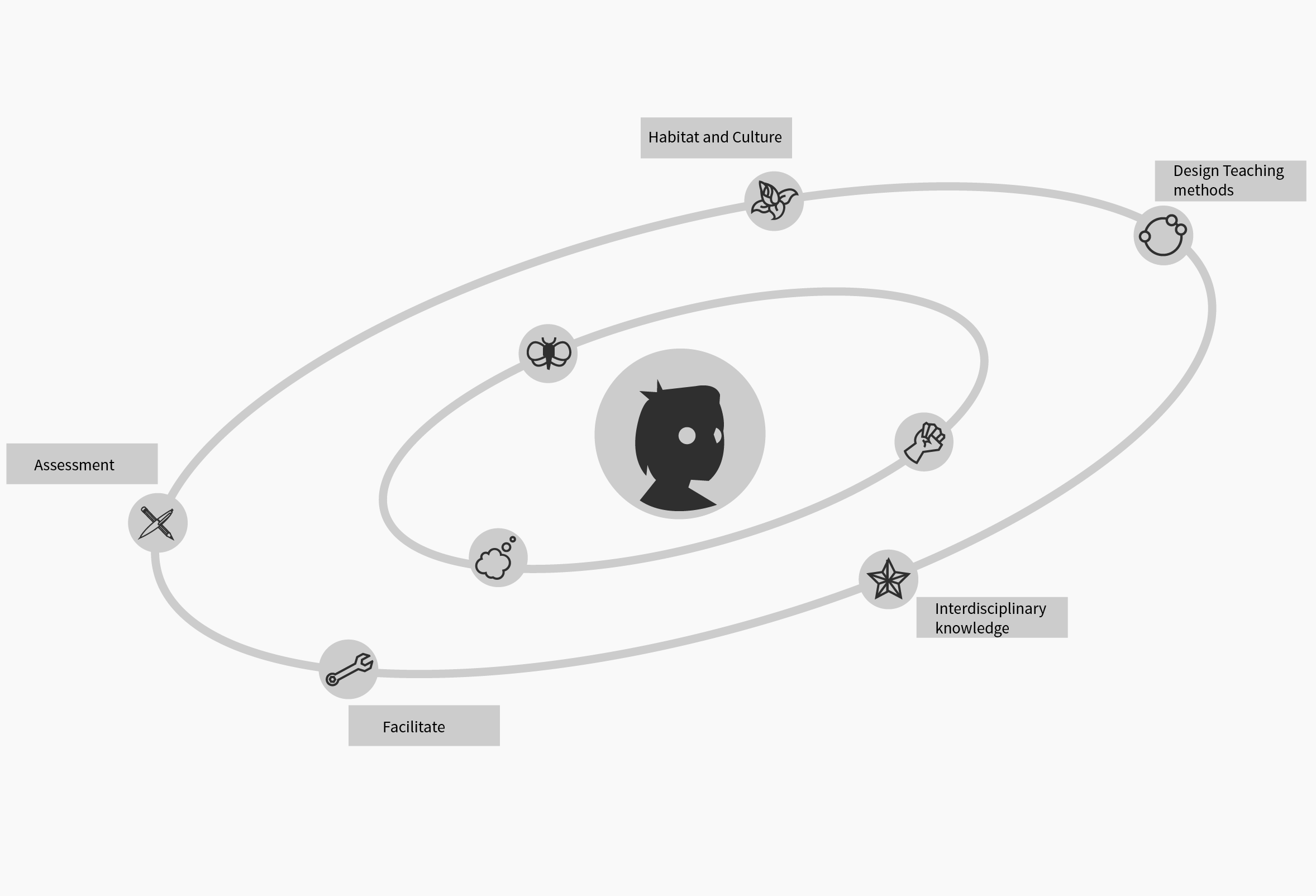
In the attempt of changing the student’s from being passive receivers of theoretical knowledge to being active creators of knowledge and primary agents in their own education process, the DesUni model offers a universe for teachers to work with in helping the students to change (Figure 1).
Figure 1. The DesUni model
Analogous with a universe, the ‘sun’ of the DesUni teaching model is the student, encircled by two sets of planetary rings. The inner ring’s three planets that spin around the student represent processes within the individual student in the learning process. The three inner planets support and stimulate the student’s actions, imagination and mind-set.
The five planets of the outer ring illustrate the external instruments and tools that assist teachers in bringing out design-oriented actions and thinking in their students when they work with the curriculum. The five outer planets of the universe are for the teacher’s work; the intention being to change the student’s expectations from being passive receivers of theoretical knowledge to becoming active creators of knowledge and primary agents in the teaching process.
If you want to see the videos that explain DesUni model, methods and theory in detail, click here…
1. Action
In order for students to be less passive in the teaching process the DesUni model is made up of factors related to inner and outer processes. The factors in the DesUni model are about putting the students in a Design-Thinking frame of mind in the teaching process, so as to change their expectations from being passive receivers of theoretical knowledge, to becoming active creators of knowledge and the primary agents in the teaching process.
Design requires action and experimentation to construct new knowledge, solve wicked problems and create preferred futures.
Changing a student’s frame of mind, through Design-Thinking, requires design action and experimentation to develop something new. However, the inner elements of the DesUni model can be hard for the teacher to change without support from the outer elements.
Literature
Seelig, T. (2012), InGenius: A Crash Course on Creativity. New York: HarperCollins.
2. Imagination
In order for students to be less passive in the teaching process, the DesUni model is made up of factors related to inner and outer processes. The factors in the DesUni model are about putting the students in a Design-Thinking frame of mind within the teaching process in order to change their expectations from those of being passive receivers of theoretical knowledge, to becoming active creators of knowledge and the primary agents in the teaching process.
Imagination is the catalyst for a design-oriented mind-set and the act of designing.
In order to change the student’s frame of mind by Design-Thinking, imagination is required as the catalyst for Design-Thinking and the act of designing; design cannot happen in the absence of imagination. At the same time the inner elements of the DesUni model can be hard for the teacher to change without support from the outer elements.
Literature
Seelig, T. (2012), InGenius: A Crash Course on Creativity. New York: HarperCollins.
3. Mind-set
In order for students to be less passive in the teaching process, the DesUni model is made up of factors related to inner and outer processes. The factors in the DesUni model are about putting the students in a Design-Thinking frame of mind within the teaching process, in order to change their expectations from those of being passive receivers of theoretical knowledge, to becoming active creators of knowledge and the primary agents in the teaching process.
The purpose is for students to have the mind-set of a designer and thus think like designers in their work with the curriculum.
Changing the student’s frame of mind requires a specific mind-set to be active, so as to develop something new and imaginative, which can be accessed through Design-Thinking. However, the inner elements of the DesUni model can be hard for the teacher to change without support from the outer elements.
Literature
Seelig, T. (2012), InGenius: A Crash Course on Creativity. New York: HarperCollins.
The inner elements of the DesUni model can be hard for the teacher to change without support from the outer elements. The intention of the outer elements is to create a learning environment that stimulates students in activating a Design-Thinking mind-set, actions and imagination in their work with the curriculum, in order to change the student’s expectations from those of being passive receivers to becoming active creators of knowledge. Therefore the elements of the universe are interrelated parts forming a whole: the same is true for the DesUni teaching model. The model offers a comprehensive teaching universe to teachers that takes into account key processes of the learning situation (e.g. assessment, habitat and culture, teaching methods), and the interface between them. So, the DesUni name also refers to what the model offers you, teachers i.e. a wide-ranging teaching universe grounded in design theory.
To learn more about the methods click here…